Precision Technology Advancements In Aerial Application

By Brad Fritz, USDA Agricultural Research Service agricultural engineer
Precision agriculture is an approach to modern farming focused on optimizing resources, enhancing productivity and minimizing environmental impact.
Agricultural aviation is a key component of precision agriculture. GPS, a technology required for precision application, has been used in agricultural aviation for more than 30 years. The agricultural aviation industry treats 127 million acres of cropland aerially each year—about 28% of U.S. cropland.
Aerial application is often the only, or at least the most economical, method for timely pesticide application. It permits large areas to be treated rapidly and far faster than any other form of application allows. When wet fields or weather conditions prevent use of other treatment methods, aerial application may be the only method available to treat pest pressure that does not harm the crop or compact the soil.
Precision in aerial application includes using GPS guidance systems to provide accurate navigation information. This technology enables pilots to maintain consistent flight paths across the field and ensure uniform application across the whole site. Variable-rate application technology via prescription mapping and flow control systems allows for aerial site-specific applications by adjusting rates on the fly to ensure optimal crop input use while reducing potential waste or environmental harm.
The same technology is also used to apply a constant rate of nutrients and plant protection products uniformly across the field.
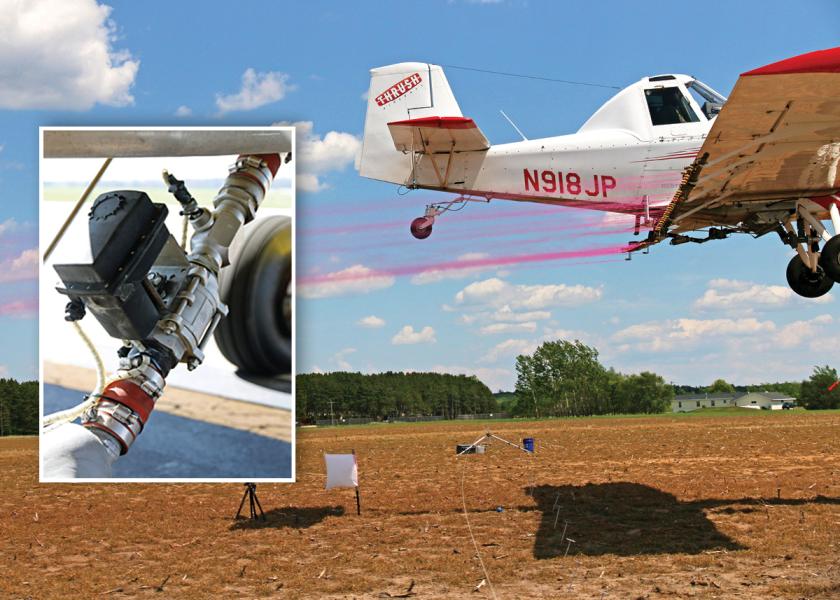
Onboard flight weather data systems constantly monitor wind speed, wind direction, temperature and humidity. Brand-new aerial technology couples the weather monitoring systems with electronic control of individual nozzles. This allows for adjusting nozzle flow in real time during the application as wind speed and direction change, and it further improves the precision of aerial pesticide applications.
Technology is in development to incorporate the AGDISP model, a software application that predicts on- and off-target movement of spray from agricultural aircraft. The combination of GPS, onboard weather systems, individual nozzle control and software capable of analyzing the data and then controlling the spray system accordingly will result in the most precise applications possible in agriculture.
The USDA Agricultural Research Service’s Aerial Application Technology Research Unit provides spray nozzle models for professional aerial applicators to assist in the selection of setups that meet the droplet size and nozzle flow rate requirements for a given application. Choosing the appropriate spray droplet size and flow rate is important for ensuring proper spray coverage on the target and minimizing off-target movement.
Even if you release spray at a precise location in the field, you haven’t made a precise application if all the spray does not reach the target or runs off the plant.
The field of aerial application continues to focus on increasing the precision and accuracy of applications on cropland. It is working toward the overall goal of greater efficiency, productivity and ecological duty.