15% Of Corn Growers Report Moderate To Severe Rootworm Issues
If you saw a lot of corn rootworm (CRW) beetles on your combine windshield this fall while harvesting soybeans, plan to protect your 2019 corn crop from the pest.
“That and beetles in your bean fields this season say your fields are at risk, and hybrid selection needs to be a big consideration for the year ahead,” says Ken Ferrie, Farm Journal Field Agronomist.
Bayer Monsanto research from 2016 and again in 2017 shows that rootworm hot spot areas are of particular concern and most prominent in northwest Illinois, northern Iowa, northeast Nebraska and northeast Colorado.
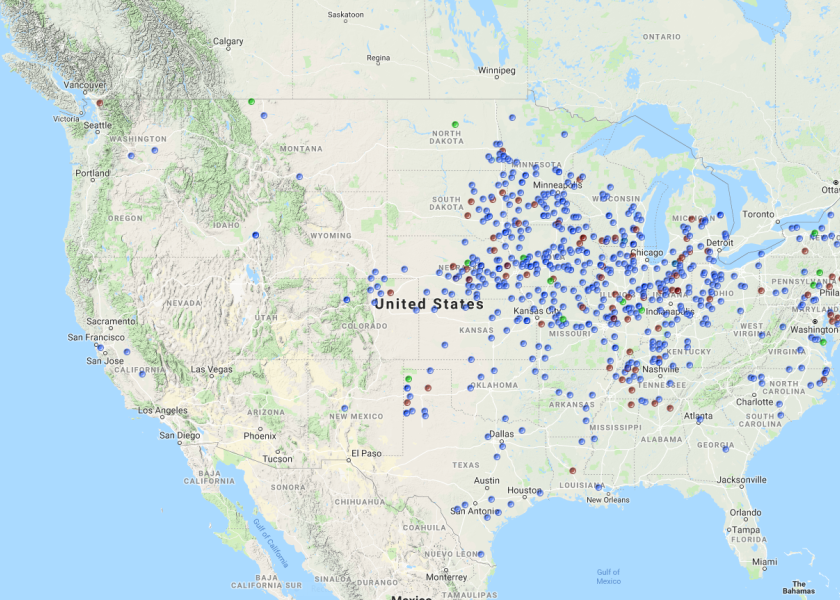
A Farm Journal Pulse survey conducted in 2018 supports that finding. The survey, conducted in November, asked farmers whether their corn rootworm infestation this year was severe, moderate or no problem. While 85% reported no problem, 15% of the 704 farmers responding said they had moderate to severe problems. A look at the map below shows the approximate location of the farmers responding, corroborating Bayer Monsanto’s findings.
Researchers say these areas of the country are routinely affected by CRW infestations, because they have a long history of continuous corn planting to accommodate livestock feeding or high-production, irrigated fields.
Annually, CRW threatens an estimated 50 million acres of U.S. cornfields, costing producers about $200 million each year in preventive measures and $800 million in yield loss. Research shows every root node nibbled by larvae results in a yield loss of about 15%. In addition, weakened roots can impede harvesting, further reducing grain yield by 15% to 34%, Bayer Monsanto reports.
With some corn traits struggling to keep CRW at bay, it’s more important than ever to use best management practices, per the National Corn Growers Association Take Initiative program:
- Plant the required refuge. Take into account the product and geography you’re in: corn-growing states’ refuge is 5% in-bag or a 20% structured refuge, and cotton-growing states are 20% in-bag and 50% for a structured refuge.
- Use insect resistance management strategies: rotate crops, use pyramided traits, rotate traits and rotate and use multiple modes of action for insecticide seed treatments, soil-applied insecticides and foliar-applied insecticides.
- Actively scout to see if control methods are working, and whether there are escapes or possible resistance. Take additional action to control pests when necessary.