Unspoken Truths About Pests: Corn Rootworm

Resistance and continuous corn are boosting populations of this yield-robbing pest
Corn rootworms can pack a one-two punch. The larvae can burrow in soil and feed on unsuspecting corn roots, or the adult beetles can snip silks and upend pollination. Both infiltrations result in lower yields.
Two types of corn rootworms wreck the most havoc in the Midwest: northern corn rootworm and western corn rootworm, says Nick Seiter, University of Illinois Extension field crops entomologist.
“The western corn rootworm was dominant for many years in Illinois, but in recent years the northern corn rootworm has crept back up in population,” he says.
RESISTANCE ISSUES
One of the reasons rootworm pressures are increasing, after several years of low numbers, is resistance or partial resistance is common to the Cry3 proteins (Cry3Bb1, mCry3A and eCry3.1Ab), Seiter says. Reduced corn rootworm susceptibility, he adds, also exists to Cry34/35Ab1, but that problem is not as widespread.
Corn rootworms most often show up in cases of continuous corn, late-maturing hybrids, delayed and/or replanted fields, weedy fields and soybeans with significant volunteer corn, says Erin Hodgson, Iowa State University Extension entomologist.
In years with adequate moisture, you likely won’t see the above-ground signs of the root-clipping larvae.
“You probably won’t see any lodged corn, and you probably will see ears that are filled out pretty good,” she adds. “You often won’t see signs of increasing injury and declining yield until the end of the season.”
Farmers need to dig up corn plants and evaluate root nodes for damage. “Root nodes contribute to nutrient and water uptake; when nodes are pruned, plant vigor is compromised and yields drop,” Hodgson says.
When evaluating rootworm damage, measure how much of the root mass has been pruned to within 1.5" of the base of the root, Seiter says.
“We rate the interior three nodes of roots for rootworm damage,” he says. “For example, one entire node of roots pruned away would be a root damage rating of 1, three entire nodes pruned would be 3, a quarter of one node pruned would be a 0.25.”
This rating system allows you to quantify and compare rootworm damage among fields.
A rating of 0.5 (one half of one node pruned) is considered unexpected damage to a pyramided Bt corn plant, and could be evidence of resistance, Seiter says.
Severe pruning of a single root node contributes to 15% yield loss, Hodgson adds.

ADAPTABLE AND DEADLY
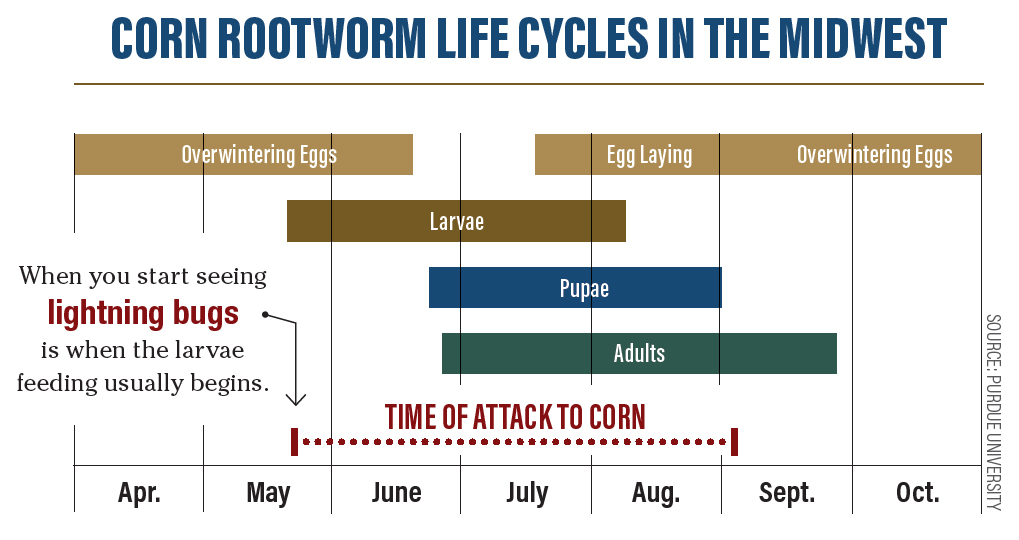
The life cycle for northern corn rootworm and western corn rootworm typically consists of one generation per year, with females laying eggs in cornfields to overwinter and hatch the following year.
However, some of these adaptable pests might wait and hatch in year two, year three or year four, Seiter says.
“Those that hatch in year two are likely to hatch into corn and start the cycle again,” he says.
Regardless, Seiter says, crop rotation is a strong management tool. Soil insecticides are also effective. The key is regular monitoring of your rootworm population.
Fast Facts About Corn Rootworm
Northern Corn Rootworm:
- Tan to pale green color.
- About ¼" long.
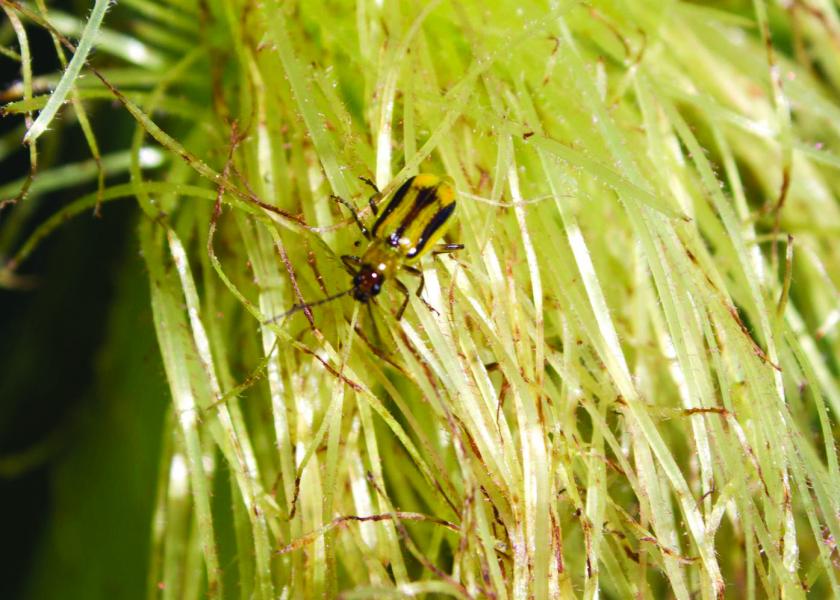
Western Corn Rootworm:
- Yellow to green color.
- Black stripe along the sides of their wing covers.
- About 5/16" long.
Southern Corn Rootworm:
- Yellow to green color.
- 11 black spots.
- About 3/8" long.
- Also known as the spotted cucumber beetle.
Both the western and northern corn rootworms cause damage to corn as larvae and adults.
Read more from this series, which shares insights on how to control pest problems.